How to operate a drone is a question many ask, venturing into the exciting world of aerial photography and videography. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, from understanding basic drone components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques and ensuring safe operation. We’ll explore essential controls, camera operation, legal considerations, and troubleshooting common issues, empowering you to confidently take to the skies.
Whether you’re a novice or seeking to enhance your skills, this guide offers a structured approach to mastering drone operation.
We’ll cover everything from selecting the right drone and understanding its various parts to mastering complex maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial footage. Safety and legal compliance will be paramount throughout our discussion, ensuring responsible and enjoyable drone piloting.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities and overall performance. This section details the function of major drone components, battery types, and motor comparisons.
Drone Component Functions
A drone comprises several key components working in harmony. The propellers generate thrust, powered by motors controlled by a flight controller. The battery provides power, while GPS aids navigation, and the camera captures imagery.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate lift and thrust, propelling the drone through the air. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: These convert electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy to spin the propellers. Brushless motors are generally preferred for their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, this sophisticated electronic board manages all aspects of flight, receiving data from sensors and executing commands from the remote control.
- Battery: This provides the electrical power needed for the motors and other onboard electronics. Battery type significantly impacts flight time and performance.
- GPS: This system uses satellite signals to determine the drone’s location, enabling features like autonomous flight and return-to-home functionality.
- Camera: This captures photos and videos, offering various features depending on the model. Resolution, shutter speed, and aperture are key adjustable parameters.
Drone Battery Types and Flight Time
Drone batteries are typically Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries, characterized by their high energy density. Different LiPo battery configurations impact flight time. Larger capacity batteries (measured in mAh – milliampere-hours) provide longer flight times but also increase weight.
- LiPo Battery Characteristics: LiPo batteries are known for their high energy density, making them ideal for powering drones. However, they require careful handling and storage due to their flammability.
- Capacity and Flight Time: A higher mAh rating generally translates to a longer flight time. For example, a 5000mAh battery will typically provide longer flight than a 3000mAh battery, all other factors being equal.
- Voltage and Flight Performance: Battery voltage (typically 3S, 4S, or 6S) influences the power available to the motors. Higher voltage batteries usually lead to faster speeds and more powerful maneuvers.
Brushless vs. Brushed Motors
Drone motors are either brushed or brushless. Brushless motors are more efficient, powerful, and longer-lasting than brushed motors, making them the standard in modern drones.
- Brushless Motors: These are more efficient, quieter, and generate less heat than brushed motors, leading to longer flight times and improved performance. They are also more durable and require less maintenance.
- Brushed Motors: These are simpler and less expensive but less efficient, produce more heat, and have a shorter lifespan than brushless motors. They are generally found in less expensive or smaller drones.
Drone Model Comparison
The following table compares the features and specifications of three different drone models. Note that these are illustrative examples and actual specifications may vary.
| Feature | Drone Model A | Drone Model B | Drone Model C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camera Resolution | 4K | 1080p | 4K |
| Flight Time (approx.) | 25 minutes | 20 minutes | 30 minutes |
| Maximum Speed | 70 km/h | 60 km/h | 80 km/h |
| Weight | 750g | 500g | 900g |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for safe and efficient drone operation. This involves calibrating the drone’s sensors, checking weather conditions, and performing a visual inspection of the drone itself.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, follow this comprehensive checklist:
- Battery Check: Ensure the battery is fully charged and securely connected.
- Propeller Inspection: Check for damage or looseness on all propellers.
- GPS Signal Acquisition: Allow sufficient time for the drone to acquire a strong GPS signal (typically indicated by a solid GPS indicator light).
- Compass Calibration: Calibrate the compass by following the manufacturer’s instructions (usually involves rotating the drone in a figure-eight pattern).
- Sensor Calibration: Check for any sensor errors reported by the drone’s software.
- Visual Inspection: Carefully inspect the drone for any visible damage or loose parts.
- Weather Check: Verify that weather conditions are suitable for flight (avoid strong winds, rain, or snow).
- Flight Area Assessment: Ensure the flight area is clear of obstacles and people.
- Remote Control Check: Verify that the remote control is fully charged and properly connected to the drone.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Accurate compass and sensor calibration is critical for stable and predictable flight. Inaccurate calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior. Always follow the manufacturer’s specific instructions for calibration.
Weather Conditions
Weather significantly impacts drone flight. Strong winds can make controlling the drone difficult, while rain or snow can damage the electronics. Always check the weather forecast before flying and postpone if conditions are unfavorable.
Pre-Flight Visual Inspection
A visual inspection is essential to identify any potential issues before flight. Check for damage to the propellers, arms, body, and any other visible components. Ensure all screws and fasteners are tight and secure.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to safe drone operation. This section details the function of control sticks, procedures for takeoff, hovering, landing, and basic maneuvers.
Control Stick Functions
Most drone remote controls use two joysticks. One joystick typically controls the drone’s altitude and direction, while the other controls its lateral movement (forward, backward, left, right).
- Left Stick (Altitude and Direction): Up/Down controls altitude, Left/Right controls yaw (rotation).
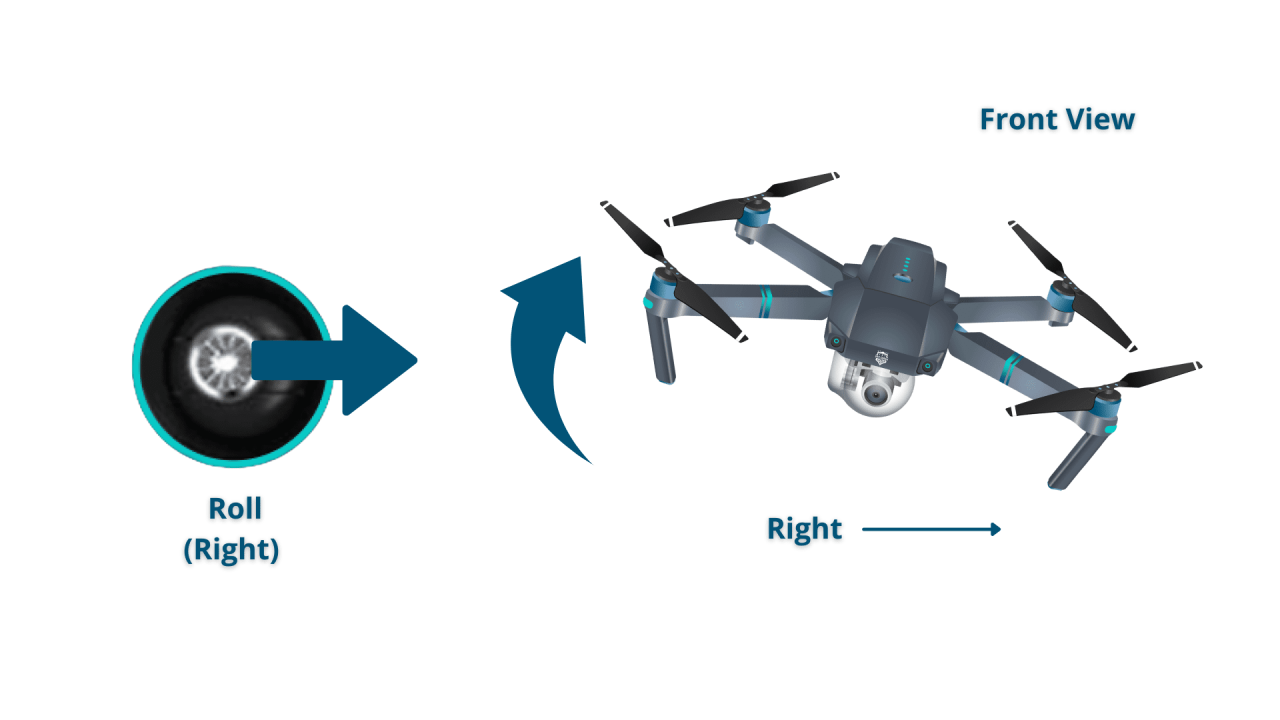
- Right Stick (Lateral Movement): Forward/Backward controls pitch (forward/backward movement), Left/Right controls roll (side-to-side movement).
Takeoff, Hovering, and Landing
These are fundamental flight procedures. Smooth and controlled execution is crucial for safety.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
- Takeoff: Gently push the left stick upwards to initiate ascent. Maintain a steady upward movement until the desired altitude is reached.
- Hovering: Once at the desired altitude, carefully adjust the stick inputs to maintain a stable position in the air. Slight adjustments are often needed to counteract wind and other factors.
- Landing: Gently lower the left stick to initiate descent. Reduce speed as you approach the ground to ensure a smooth landing.
Altitude and Direction Control
Precise altitude and direction control is achieved through careful manipulation of the left joystick. Smooth, controlled movements are key to avoiding abrupt changes in flight path.
Common Flight Maneuvers

These basic maneuvers form the foundation for more advanced flight techniques.
- Turning: Use the left joystick to control yaw (rotation) to turn the drone left or right.
- Ascending: Push the left joystick upwards to increase altitude.
- Descending: Pull the left joystick downwards to decrease altitude.
- Moving Laterally: Use the right joystick to control roll and pitch to move the drone forward, backward, left, or right.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic flight, more advanced maneuvers can be explored. These require practice and a good understanding of drone control.
Complex Maneuvers
These maneuvers add dynamic elements to your flights, but require careful control and practice to execute safely.
- Flips and Rolls: Many drones offer pre-programmed acrobatic maneuvers like flips and rolls. These are usually activated through buttons on the remote control.
- 360-Degree Rotations: This maneuver involves smoothly rotating the drone 360 degrees around its vertical axis.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions requires more skill and attention. Adjustments to control inputs are often necessary to counteract wind gusts.
- Wind Compensation: Anticipate wind gusts and make appropriate adjustments to the control sticks to maintain stability.
- Lower Altitude: Flying at lower altitudes can reduce the impact of wind.
- Avoid Strong Winds: It is best to avoid flying in strong winds altogether.
Waypoints and Autonomous Flight
Many drones support waypoint navigation, enabling autonomous flight. Waypoints are pre-defined locations the drone will automatically navigate to, allowing for complex flight plans.
Flight Plan Example
A simple flight plan might involve taking off, flying to waypoint A, capturing a photo, moving to waypoint B, circling once, and then returning to the starting point for landing.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
The camera is a key feature of many drones, enabling high-quality aerial photography and videography. Understanding camera settings and techniques is crucial for capturing compelling imagery.
Camera Setting Adjustments
Camera settings such as resolution, shutter speed, and aperture can significantly impact the quality of your photos and videos. Experiment to find the optimal settings for your specific conditions.
- Resolution: Higher resolution (e.g., 4K) results in more detail but larger file sizes.
- Shutter Speed: Adjust shutter speed to control motion blur. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds can create a sense of movement.
- Aperture: Aperture affects depth of field. A wider aperture (lower f-number) results in a shallower depth of field, blurring the background.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Capturing high-quality aerial footage requires careful attention to detail. Consider factors like lighting, composition, and stability.
Stable Shots and Avoiding Camera Shake
Maintaining a stable camera is essential for smooth, professional-looking videos. Use features like electronic image stabilization (EIS) or mechanical gimbal stabilization to minimize camera shake.
Post-Processing Drone Footage
Post-processing can enhance your drone footage. Software like Adobe Premiere Pro or DaVinci Resolve allows for color correction, stabilization, and other enhancements.
- Import Footage: Import your drone footage into your chosen editing software.
- Color Correction: Adjust colors to achieve a consistent and pleasing look.
- Stabilization: Apply stabilization effects to smooth out any shaky footage.
- Editing and Effects: Add transitions, music, and other effects to enhance your video.
- Export: Export your finished video in the desired format and resolution.
Safety and Legal Considerations
Safe and responsible drone operation is paramount. This involves understanding potential hazards, adhering to relevant laws and regulations, and maintaining a safe distance from people and obstacles.
Potential Hazards
Drone operation carries potential hazards, including collisions with objects or people, battery fires, and loss of control.
Laws and Regulations
Drone laws and regulations vary by location. It’s crucial to research and comply with all applicable laws in your area before flying.
Safe Distance from People and Obstacles
Maintain a safe distance from people and obstacles at all times. Never fly over crowds or sensitive areas.
Safety Tips for Responsible Drone Operation
- Always check weather conditions before flying.
- Never fly near airports or other restricted airspace.
- Keep the drone within visual line of sight.
- Always have a backup battery.
- Follow all applicable laws and regulations.
- Never fly under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
- Be aware of your surroundings at all times.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even with careful operation, drone malfunctions can occur. This section provides solutions for common problems and emphasizes the importance of regular maintenance.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Here are solutions for some common drone issues:
- Low Battery Warning: Land the drone immediately and replace or recharge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with a clear view of the sky and restart the drone.
- Motor Malfunctions: Check for obstructions, loose connections, or damaged motors. Contact support if needed.
- Connectivity Issues: Check for interference, ensure the remote and drone are within range, and restart both devices.
Recovering a Crashed Drone
If your drone crashes, assess the damage and attempt a safe recovery. Prioritize safety and avoid further damage during the recovery process.
Regular Maintenance and Cleaning
Regular maintenance and cleaning are crucial for extending the lifespan of your drone and preventing malfunctions. Clean propellers, check for loose parts, and inspect the battery regularly.
Drone Photography and Videography Composition
Effective composition is key to creating stunning aerial photos and videos. This section explores composition techniques and provides tips for capturing compelling footage.
Rule of Thirds and Leading Lines

The rule of thirds and leading lines are fundamental composition techniques that can greatly enhance the visual appeal of your drone shots.
Effective Shot Compositions for Different Landscapes
The optimal composition will vary depending on the landscape. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to find the most visually appealing shots.
Creating Dynamic and Visually Appealing Videos, How to operate a drone
Dynamic videos use a variety of shots, angles, and movements to keep viewers engaged.
Tips for Capturing Compelling Aerial Footage
- Use a variety of shots, including wide shots, close-ups, and tracking shots.
- Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
- Pay attention to lighting and shadows.
- Use smooth movements to avoid jerky footage.
- Edit your footage to create a compelling narrative.
Mastering drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical understanding with practical skill. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of drone mechanics, safe flight procedures, and creative aerial photography and videography techniques. By consistently practicing safe operation and adhering to all relevant regulations, you can unlock the full potential of your drone, capturing breathtaking imagery and exploring new perspectives.
Remember that continued learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot.
Query Resolution
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering controls. Successfully navigating this process requires learning about airspace regulations and practicing safe flying techniques. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone which will help you confidently handle your drone. Ultimately, responsible drone operation ensures both safety and enjoyment.
For beginners, a user-friendly drone with GPS stabilization, obstacle avoidance features, and a relatively long flight time is recommended. Look for models known for their ease of use and forgiving flight characteristics.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Calibrating your drone’s compass before each flight is a best practice. This ensures accurate flight and prevents unexpected behavior. Refer to your drone’s manual for specific calibration instructions.
What is the best way to store my drone battery?
Store your drone batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Store them at around 50% charge to maximize their lifespan.
How do I handle a drone malfunction during flight?
If a malfunction occurs, prioritize safety. Attempt a controlled descent or emergency landing according to your drone’s manual. If the drone is uncontrollable, immediately switch it off.
